Krishna Kumar M1*, Aboorva S2, Priyadarshini V2 and Ananda Kumar B3
1 Professor of Radiology, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Trichy SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Irungalur, Trichy, India
2 Postgraduate Student and Resident, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Trichy SRM Medical college hospital and Research Centre, Irungalur, Trichy, India
3 Assistant Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Trichy SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Irungalur, Trichy, India
*Corresponding Author: Krishna Kumar M, Professor of Radiology, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Trichy SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Irungalur, Trichy, India.
Received: January 12, 2023; Published: February 07, 2023
Citation: Krishna Kumar M., et al. “Radiological Imaging Features of Wilson’s Disease in an Early Adolescent Male: Case Report”. Acta Scientific Paediatrics 6.3 (2023): 09-15.
Inborn defect in the copper metabolism leads to Wilson’s disease (WD) with an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. Abnormal accumulation of copper in various tissues is caused by ATP7B mutation. In individuals affected by WD, however, impaired copper metabolism and excretion leads to the deposition of redundant free copper in the brain, liver, cornea, kidney and other organs, resulting in organ damage. Diagnosis of WD is made based on various neurologic and hepatic clinical symptoms, Kayser-Fleischer (K-F) rings in the cornea and biochemical tests for copper. Neurological manifestations of WD include pyramidal and extrapyramidal features, as well as cognitive and psychiatric symptoms. Earlier diagnosis and intervention are necessary for patients with WD. Both clinical symptoms and neuroimaging abnormalities are partially reversible with anti-copper treatment. Radiological imaging features were evaluated in a 13 years old preadolescent male with WD, who presented with involuntary movements of extremities, drooling of saliva, dysarthria, vomiting, itching and behaviour disorders for the past 45 days.
Keywords: Hepatolenticular Degeneration; Kayser-Fleischer Rings; Wilson’s Disease.
Wilson’s disease (WD) also known as Hepatolenticular degeneration (HLD), is due to a defective function of the enzyme ATPase 7B in hepatocytes which causes reduced excretion of copper into bile [1,2].
WD is known to be more prevalent amongst the Chinese and other Asian populations with incidence varying from 1/30,000- 1/10,0000 and carrier frequency roughly about 1/90 [3].
WD is traditionally considered a disease of children and young adults. Abnormal accumulation of copper causes damage to various organs resulting in broad-ranging clinical symptoms, especially dominated by signs of brain damage (mainly basal ganglia and cerebellum) and liver.
Of the WD, neurologic presentation accounts for 40-60% [4,5]. WD is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical and diagnostic tests including presence of corneal Kayser-Fleisher (K-F) rings, decreased serum ceruloplasmin, and 24 hours increased urinary copper excretion [6,7]. If WD is diagnosed early, prior to the development of more severe damage, especially to the liver and brain, it is treatable.
The purpose of the study was to describe the range of abnormalities seen on radiological imaging of early adolescent male patient with WD and correlate with clinical findings.
An early adolescent male aged 13 years presented with involuntary movements of extremities, drooling of saliva, dysarthria, vomiting, itching and behaviour disorders for the past 45 days duration.
He was diagnosed to be suffering from WD at the age of 7 years and was on irregular treatment. History of 2nd degree consanguineous marriage of the parents noted.
Clinical examination showed generalised dystonia involving limbs, tremor in the hands, yellowish discolouration of skin and sclera, KF ring in the eye (Figure 1). Other Vitals were unremarkable. Laboratory examination revealed reduced haemoglobin of 10.9g/dl, elevated total bilirubin (1.68), direct bilirubin (0.79) and SGOT (84). Gamma Glutamyl transferase (13 u/l) was reduced with increased urine excretion of 24hour copper of 980 ug. Peripheral smear showed macrocytic anaemia with mild thrombocytopenia. Prothrombin time (14.4 sec) and Activated Partial Thromboplastin Clotting Time (APTT) was prolonged.
WD is diagnosed based on hypocupraemia, hypo-aceruloplasminemia, 24-hour increased urinary copper , confirmed by molecular analysis, and clinically by Kayser-Fleischer rings in the cornea.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain ,showed small focal hypo intensities in bilateral basal ganglia on T1W sequences (Figure 2), small focal hypo intensities with minimal surrounding hyperintensities in bilateral basal ganglia on T2W and FLAIR (Figure 3), small focal areas of blooming in bilateral basal ganglia on T2W gradient echo (GRE) images (Figure 4), small focal hypointensities with minimal surrounding area of restricted diffusion in bilateral basal ganglia in diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and No contrast enhancement in these regions (Figure 5).
Computed Tomography (CT) of brain revealed small focal hypodensities in bilateral basal ganglia with tiny calcifications in bilateral lentiform nucleus (Figure 6).
Ultrasonogram (USG) examination of abdomen revealed Chronic liver parenchymal disease (Figure 7) and Splenomegaly (13.6 centimetre).
Diagnosis of WD was confirmed, based on the clinical, laboratory and imaging findings.
Historically, in 1912 Wilson first noted the neurologic symptoms of WD and provided detailed accounts of the clinical presentation, including descriptions of various movement disorders, drooling, dysarthria and psychiatric symptoms in 12 patients [8].
WD is characterized by abnormal accumulation of copper in various tissues, particularly in the liver and the brain caused by uncommon, autosomal recessive, inborn defect in copper metabolism.
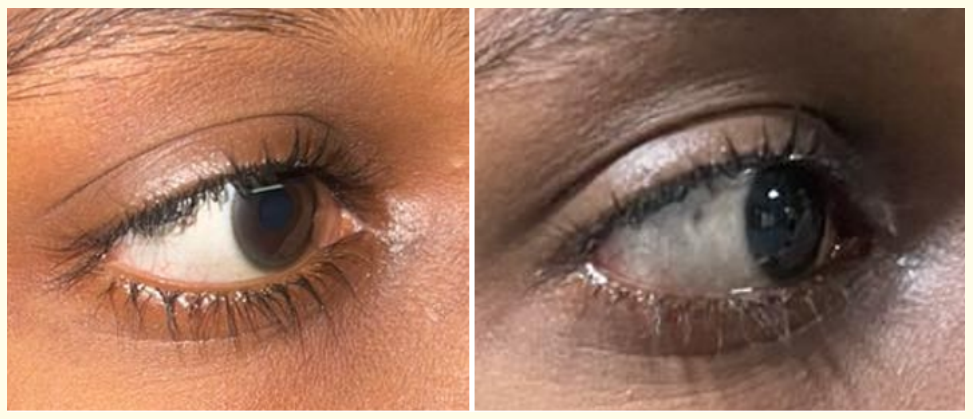
Figure 1: (A, B): 13 years old early adolescent male with WD, eyes showing thin rim of brown coloured Kayser-Fleischer (KF) rings in the cornea.
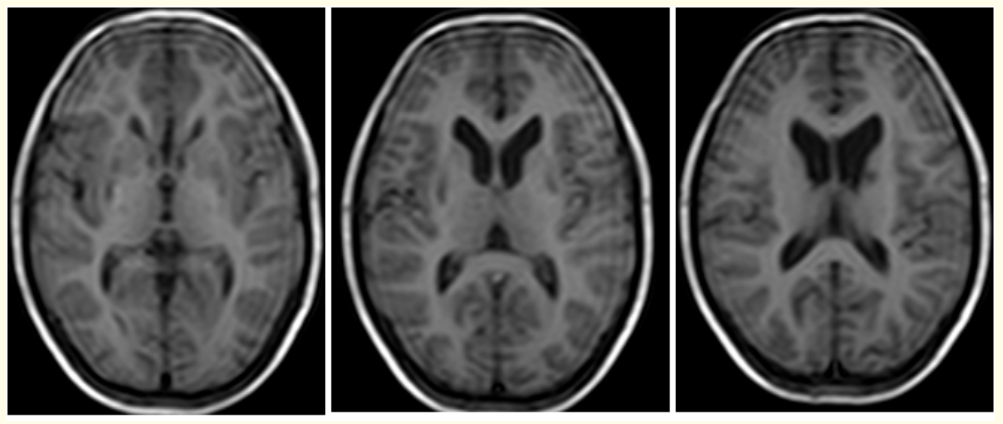
Figure 2: (A-C): Axial T1W MRI images reveal small focal hypo intensities in bilateral basal ganglia of a 13 years old male with WD.
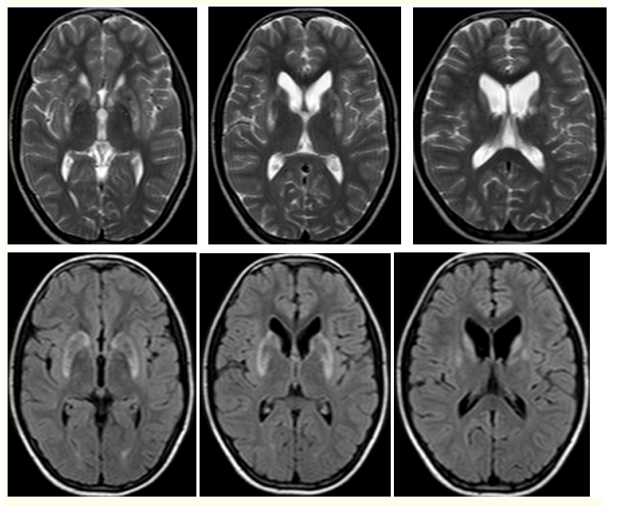
Figure 3: (A-F): T2W Axial (A-C): and FLAIR. (D-F): MR images show small focal hypo intensities with minimal surrounding hyperintensities in bilateral basal ganglia of a 13 old male patient with WD.
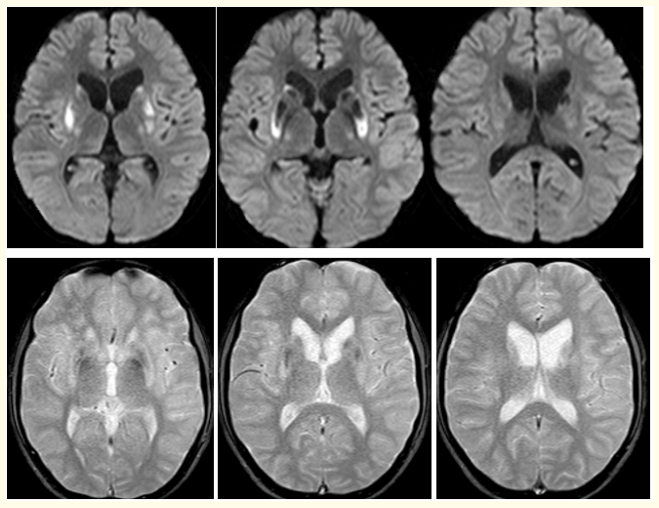
Figure 4: ( A-F): DWI (A-C): Show small focal hypointensities with minimal surrounding area of restricted diffusion in bilateral basal ganglia and T2W gradient echo images. (D-F): Reveal small focal areas of blooming in bilateral basal ganglia of a 13 years old male patient with WD.
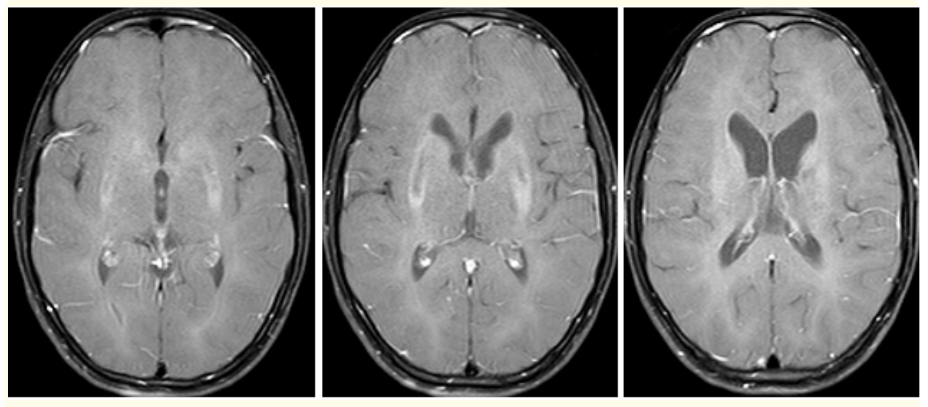
Figure 5: (A-C) Contrast enhanced MR axial images did not show any enhancing lesions of Basal ganglia in a 13 year old patient with WD.
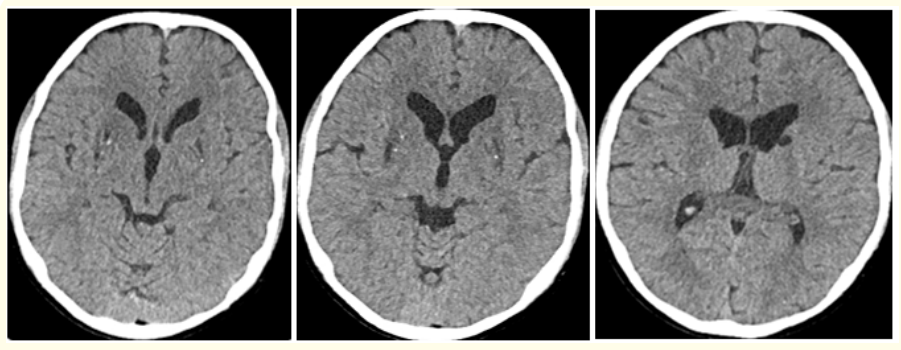
Figure 6: (A-C): Axial Computed tomography (CT) images of Brain of 13 years old male patient with WD shows small focal hypodensities in bilateral basal ganglia with tiny calcifications in bilateral lentiform nucleus.
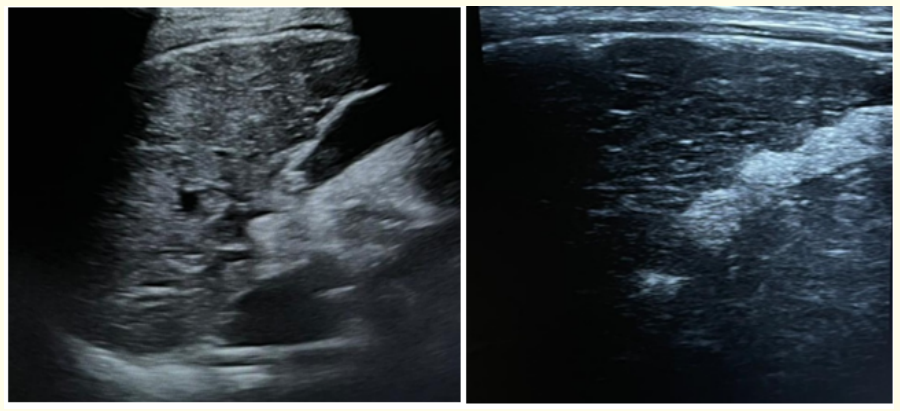
Figure 7: (A,B)Ultrasound image of 13 years old male patient with WD, showing coarse altered heterogenous echotexture of liver with nodular surface contours.
ATP7B is the pathogenic gene, situated at chromosome 13q14.3 which, encodes for a copper-transporting ATPase that facilitates the combination of copper and Alpha 2-globulin into ceruloplasmin in liver, a process that is responsible for the elimination of 90% of the copper found in the circulation in normal individuals [9].
In individualities affected by WD, still impaired copper metabolism and excretion leads to the deposition of redundant free copper in the brain, liver, cornea, kidney and other organs, resulting in organ damage [10].
WD is less commonly seen in women than in men. The most common age of onset WD is between 5 - 35 years, reflecting the potential copper storage capacity of the liver [11]. Multiple studies showed that the youngest age of onset of WD was 3 and the oldest age was 80 years [12,13]. Our patient age at onset was 7 years and presented to us at 13 years which correlates with the former study [11].
WD Clinically, presents with neurologic, hepatic, or psychiatric manifestations or their combinations. WD neurologically may manifest with pyramidal and extrapyramidal features, as well as cognitive and psychiatric symptoms. WD is one of the few hereditary conditions that shows significant improvement of symptoms and responds well to treatment, with a regular regimen of de-coppering agents [14].
The foremost symptoms of WD are dysarthria and difficulty with the hands [15], but personality and psychiatric problems develop latterly, together with neurologic abnormalities that can be grouped into four common clinical types: Parkinsonian, pseudo sclerotic (tremor, dysarthria, and ataxia), dystonic, and chorea. The extrapyramidal system is complex but in a simplified form can be thought of as having a major circuit through the cortex, lentiform nuclei, caudate, and thalamic nuclei and minor circuits involving the lentiform nuclei, subthalamic nuclei, substantia nigra, pons, cerebellum, middle cerebellar peduncles, and red nuclei [4]. The symptom of torsion spasm in WD seems to indicate abnormalities in the midbrain and cortex and, the symptom of choreoathetosis generally suggests damage in the caudate nucleus.
Histopathologic studies of the cerebral system in WD have shown abnormalities throughout with atrophy, spongy softening, cavitation, general reduction of neurons, increased cellularity, and the presence of Opal ski cells [16].
In our study, early adolescent male of 13 years was suffering from WD with extrapyramidal pseudo sclerotic symptoms (dysarthria and ataxia), hepatic dysfunction and behaviour disorders for a duration of 6 years with irregular treatment and intermittent symptoms when treatment was stopped.
In WD, accumulation copper in brain causes neurologic symptoms associated with neuroimaging abnormalities best visualized by cerebral MRI. In former reports, the most constantly linked MR imaging abnormality was bilateral symmetric hyperintensity in the putamen on T2W images [17,19,36].
In a study by Kim., et al. [18] high-signal-intensity lesions on T2W images were most constantly located in the putamen (83%), followed by the caudate nucleus (67%), globus pallidus (58%), thalamus (50%), midbrain (42%), pons (8%) and 42% showed T2W dark signal intensity in the globus pallidus, putamen, or caudate nucleus, surrounded by peripheral high signal intensity. In WD, it has been noticed that the phagocytes containing iron pigment were seen in the globus pallidus and substantia nigra [19], which explains T2W dark signal intensity.
Our study showed dark signal intensity in the globus pallidus, putamen, and caudate nucleus, surrounded by peripheral high signal intensity on T2W and FLAIR images (Figure 3), anologous to the study by Kim., et al. [18] and Dosek P., et al. [20].
T2W hyperintensities in the deep gray matter (DGM), brainstem, and cerebral white matter (WM) and T2W hypo intensities in the DGM and global atrophy are the abnormal findings at MRI [20]. T2W hypo intensities and atrophy are largely irreversible and may even progress after treatment initiation, whereas T2W hyperintensities are reversible with treatment, [21,22]. Generalized susceptibility and longstanding effect of the copper intoxication on central nervous system leads to diffuse brain atrophy.
At brain MRI, a semiquantitative scale for visual assessment of WD severity was developed and validated lately [21]. Accordingly, it is made of 2 scores 1) the acute toxicity score-representing the extent of T2W hyperintensities and 2) chronic damage score- representing the extent of atrophy and T2W hypo intensities. The extent of neurologic symptoms correlated substantially with the chronic damage score [21].
Other 3 established MRI signs that could help us to prove the diagnosis include 1) “face of giant panda sign” (T2W hyperintensity in the tegmentum of midbrain, hypo intensity of the superior colliculus and normal signal intensity of red nuclei and lateral portion of the pars reticulata of the substantia nigra), 2) “face of the miniature panda sign” or “trident sign,” or “panda cub sign” seen in the pontine tegmentum (eyes of the panda -T2W relative hypo intensity of the medial longitudinal fasciculi and central tegmental tract, nose and mouth of the panda-T2W hyperintensity of the aqueduct opening into the fourth ventricle, bounded inferiorly by the superior medullary velum) and 3) “bright claustrum sign” ( T2W hyperintense thin rim in lateral part of claustrum) [23-25].
Brain lesions may be present in multiple spots in WD, exhibiting symmetrical abnormal signal in bilateral hemisphere [26]. The white matter was constantly also involved in the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes regardless of whether cortex lesions were observed, with the former presenting as a diffuse abnormal signal extending from the frontal to the occipital lobe [28]. In addition, WD lesions could also involve corpus callosum [29] and the conduction tracts, including the cerebellopontine, corticospinal, red nucleus thalamic tracts [30].
In the present study, we found that the basal ganglia were the most commonly affected site, a finding that was consistent with a former report [27].
Several imaging, electrophysiologic, and pathologic studies indicate widespread myelin damage in WD. Methodical analysis of T2-weighted MRI scans verified WM involvement, including the corticospinal, dentate-rubro-thalamic, and pontocerebellar tracts, in more than 40% of patients with WD [30], whereas conduction time extension suggestive of demyelination was detected with somatosensory and brainstem auditory evoked potentials [31].
Abnormal T1W hyperintensity in the pons, midbrain, globus pallidus, and putamen is characteristic of chronic hepatocellular dysfunction [32,33], attributed to manganese deposits [34].
Quantitative analyses of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters have demonstrated altered tissue microstructure in normalappearing lobar WM and the thalamus [35-37].
The Unified WD Rating Scale (UWDRS) assessed the neurologic severity associated with the regularized brain volume, brain parenchymal fraction, and total volumes of Gray and white matter [38].
In recent studies, modified Young scale, assessed the disability associated with the degree of volume loss in the putamen and globus pallidus [39], whereas eye movement abnormalities in treated neurologic WD was associated with brainstem atrophy [40]. Also, T2W hypo intensities in the DGM on post mortem MRI and histopathologic study confirmed iron deposits, which correlate with neuropathologic severity [41].
Proton MR spectroscopy (MRS) can be affected by accumulation of paramagnetic copper. Leandro., et al. [42], noticed decreased NAA/Cr ratio, particularly in frontal white matter and parieto-occipital cortex, despite normal MRI. They also found increased Myoinositol (mI)/Cr ratio suggestive of gliosis.
A study by W. Zhong., et al. [43] revealed that patients with disease durations of over a year, all had abnormal MRI manifestations, and that the disease duration of MRI-abnormal patients was significantly longer than that of patients with normal MRI results, which correlated with our study.
In young patient with acute hepatitis, Basal ganglia calcification may be result of WD [44]. Hypoparathyroidism due to copper deposition in parathyroid glands has been reported in WD, which may cause secondary brain calcification [45] (Figure 6).
In comparison to other types of cirrhosis, WD involving the liver has several unique CT features which include hyperdense nodules and a honeycomb pattern in the pre-contrast scan and also in portal and parenchymal phases [46].
Ultrasonography of WD cases shows hyperechoic liver representing hepatic steato-fibrosis and irregular liver surface, thickened gall bladder walls, dilated portal vein with decreased inflow rate, portosystemic shunts, and splenomegaly are found in the case of hepatic cirrhosis. Right lobe to Caudate lobe of liver ratio equal to or >0.65 and perihepatic hyperechogenic zone suggests WD as a possible cause of cirrhosis [47] (Figure 7).
Early diagnosis and intervention for patients with WD are essential, and MRI, which retain a level of specificity and sensitivity far superior to that of CT [48], can be a particularly important tool in this regard, especially for patients presenting with initial neurological symptoms.
Chelating agents, used to ‘de-copper’ patients, such as penicillamine and Trientine, facilitate the urinary excretion of copper. Patients with neurological presentations, still have unpredictable outcomes and the majority have ongoing neurological symptoms or disability [49]. Combination of genetic new born screening and gene therapy may be the ultimate solution for WD.
Early diagnosis and intervention for patients with WD are essential, and MRI, which retain a level of specificity and sensitivity far superior to that of CT can be a particularly important tool in this regard, especially for patients presenting with initial neurological symptoms.
Follow-up MR imaging in WD patients, revealed interval changes which has a close correlation with clinical features and can be useful in assessing the clinical response to treatment. Patients with neurological presentations, still have unpredictable outcomes and the majority have ongoing neurological symptoms or disability. Combination of genetic new born screening and gene therapy may be the ultimate solution for WD.
Copyright: © 2023 Krishna Kumar M., et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ff
© 2024 Acta Scientific, All rights reserved.