Lina Viktoria Benkhardt1,2*, Mona Katharina Sprengeler2, Michael Fuchs1, Kai von Klitzing2, Sylvi Meuret1+, Franziska SchlensogSchuster2,3,+
1 Division of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Phoniatrics and Audiology, University of Leipzig, Liebigstrasse 10-14, 04103 Leipzig, Germany
2 Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, University of Leipzig, Liebigstrasse 20a, 04103 Leipzig Germany
3 University Hospital of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, University of Bern, Bollingenstrasse 111, 3000 Bern 60, Switzerland
* shared authorship: Dr. Sylvi Meuret and Dr. Schlensog-Schuster
*Corresponding Author: Lina Benkhardt, Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, University of Leipzig, Liebigstrasse 20a, 04103 Leipzig, Germany. E-mail: lina.benkhardt@medizin.uni-leipzig.de
Received: November 21, 2022; Published: January 18, 2023
Citation: Lina Viktoria Benkhardt., et al. “Relevance of Auditory and Oropharyngeal Diagnostics in Children with Feeding Disorders”. Acta Scientific Paediatrics 6.2 (2023): 02-15.
2.5% of children aged 18 months have a diagnosed feeding disorder, 1% experience oropharyngeal difficulties and 0.3% of newborns are affected by hearing loss as the most common sensory disability in childhood. This investigation describes the prevalence of hearing loss and oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with a feeding disorder and their secondary diagnoses. Additionally, the associations of a feeding disorder, hearing loss and oropharyngeal dysphagia are examined. A retrospectively reviewed sample of N = 179 children aged 0 to 6 years with a feeding disorder was analysed. Only children who submitted at least one audiometry screening or flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing were included. Sixty-three children presented hearing loss (35.2%), 14 (7.8%) oropharyngeal dysphagia and 14 (7.8%) all three disabilities. The following findings also revealed that children with a feeding disorder and hearing loss have a high coincidence with cardiovascular and syndromal diseases. The results indicate that repeated hearing examinations during early childhood are essential for children with a feeding disorder to reduce the clinical outcome of hearing loss, but flexible endoscopic evaluations of swallowing should be considered only in children with specific risk factors.
Keywords: Hearing Loss; Oropharyngeal Dysphagia; Feeding Disorder; Syndromal Diseases; Cardiovascular Conditions; Early Childhood.
FD: Feeding Disorder; HL: Hearing Loss; FEES: Flexible Endoscopic Evaluations of Swallowing; OPD: Oropharyngeal Dysphagia; e.g.: Exempli Gratia
Feeding disorder (FD), hearing loss (HL) and oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD) are common in early infancy. These impairments are increasing due to higher survival rates of infants born prematurely and with a large number of life-threatening comorbidities [14,24]. HL, in particular, is the most common sensory impairment in childhood [26,35]. Some studies have shown the simultaneous occurrence of HL and OPD in children with underlying syndromal disease [41]. Adams-Chapman., et al. [1] mentioned an independent association between FD and HL. However, despite the vast literature in this area, significant gaps exist regarding a potential relationship between the three impairments of FD, HL and OPD. This introductory chapter overviews the three impairments and possible correlations found the literature.
2.5% of 18-month-old children have a diagnosed feeding disorder, according to Skovgaard., et al. [38]. In the current ICD-10, feeding disorder (F98.2) is defined as a “refusal to eat, extreme selective eating behaviour despite an appropriate food supply and competent caregiver in the absence of an organic disease with a duration of one month, onset before the sixth year excluding other mental and organic disorders” and does not mention pre-existing conditions [13]. Regardless of this definition, risk factors such as low birth weight, previous illnesses and maternal factors may play a role in the development of FD [6]. McDermott., et al. [28] reported that 40% of the children who have been irregular eaters at age 5, are still irregular eaters at age 14. Early interventions are necessary to mitigate long-term consequences like eating disorders and behavioural deficits [4,42]. The current study by Sprengeler., et al. [39] should be mentioned here to support new treatment approaches. They investigated the presumed superiority of parent-infant psychotherapy compared to the usual care with children with regulatory disorders, mainly feeding disorders.
Similarly, to FD, HL is a common problem, especially in children with syndromal diseases [20]. Hearing loss affects 0.3% of newborns [26,35]. At the age of 5 years, the prevalence is 2.7 per 1000 children [35]. Risk factors include familial hearing impairment, intensive care >48 hours, ventilation, preterm birth, infections and deformities of the head [15,26]. Grey., et al. [19] pointed out that hearing problems influence language development and social interaction [5]. Universal newborn hearing screening is considered one of the most effective ways to detect congenital hearing disorders [19].
Studies investigating the association between FD and HL are rare. In contrast, FD and OPD are often described together or used as synonyms [14,34], especially in infants and young children [33,40]. However, it remains unclear whether authors have distinguished between a feeding problem and a feeding disorder diagnosis that meets the criteria of the ICD-10 definition [40].
The exact prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in neonates is unknown [23]. Swallowing difficulties affect about 1% of children in the general population [3]. The incidence is much higher in the presence of risk factors [23] such as laryngomalacia [37]. Other reasons for experiencing oropharyngeal dysphagia include syndromic diseases, anatomical malformations and premature birth, often linked to extended nasogastric tube feeding and long-term mechanical ventilation [24,36]. Investigations, which examine the long-term course of OPD in childhood are still missing. Some authors state an improvement in oropharyngeal swallowing symptoms over time [2], but others have not described any change [8].
There is a minimal range of studies dealing with FD, HL and OPD associations. Of course, it is known that many underlying diseases are risk factors for the development of the three impairments mentioned, but the associations between them have not been widely studied. Hearing and swallowing disorders are reported in children with cerebral palsy [41] and other syndromal disorders [25]. The studies of Malas., et al. [27] and Adams-Chapman., et al. [1] indicated a correlation between feeding or swallowing disorders and language impairment. Language difficulties can be a result of hearing problems [7].
To our knowledge, no further studies have investigated the association of the three disorders independently of a specific syndrome or a single underlying causative disease. The purpose of this paper is to address this knowledge gap. Our primary concern is to draw attention to this topic. The specific objectives include 1) to determine the prevalence of HL, OPD and both HL and OPD in our cohort of children with FD, 2) to examine the secondary diagnoses and 3) to describe the relationship between the disorders. We hypothesise that there is (A) an association between FD and HL, (B) a correlation between FD and OPD and (C) a relationship between all three disorders at a significance level of p-value <0.05.
This investigation was conducted in a single-centre tertiarycare hospital. The study was approved by the Regional Ethics Committee (380/20-ek). This chapter includes the study design, the criteria for patient inclusion and the description of the procedure, measurement details, the group assignment and the data analysis.
The researchers of this study retrospectively reviewed a comprehensive clinical database of infants and children undergoing treatment for a feeding disorder at the University Hospital Leipzig between January 2010 and December 2020.
To meet the inclusion criteria, patients were required to have a diagnosis of FD, be aged 0–6 years at the time of this diagnosis and have undergone audiometry, Flexible Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) examination or both. Thus, children who presented to our clinic with FD but did not receive HL or OPD screening were not included in our study. A total of N = 179 infants and children were eligible for inclusion.
For this study, researchers evaluated all physicians’ letters from the last ten years for each patient. First, demographics about the child were recorded, including the week of pregnancy at birth and birth complications. Further data included secondary diagnoses, number of hospitalisations and surgeries.
Data from the universal newborn hearing screening, audiology test and FEES results were also collected.
Child psychiatrists, child psychotherapists or paediatricians at the Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics of the University Hospital Leipzig were the first to treat all participants. The children were subsequently examined in the Department for Otorhinolaryngology, Division of Phoniatrics and Audiology for audiometry or/and the Flexible Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing. There were no children who initially only presented at the Department for Otorhinolaryngology, Division of Phoniatrics and Audiology and then at the Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics.
The children were diagnosed using an intensive standardised clinical examination procedure. The diagnosis “feeding disorder” (F98.2) was assigned according to the ICD-10 criteria.
To examine hearing function in our study, audiological tests were performed appropriate to the age and developmental stage of the patients (e.g. binaural free-field audiometry, play audiometry, otoacoustic emissions and electrical response audiometry).
The FEES procedure was used to assess swallowing function. It involves passing a flexible endoscope through the nose and towards the pharynx to observe swallowing in real time [9]. Examiners used the penetration aspiration scale (PAS), an 8-point scale classifying the degree of airway invasion [9].
The definitions shown in table 1 and the tests just mentioned in the Measurement part were used in our study to identify all disorders. After the evaluation of all examinations, patients were categorised into four main groups. All infants who met the ICD-10 feeding disorder diagnosis criteria and did not have HL or OPD were assigned to group 1. Even if the infants only had an unremarkable audiometry or swallowing examination and the other test (swallowing or audiometry screening) was not performed, they became part of this group. All children who met the definitions of FD and HL were part of group 2. Group 3 consisted of FD and OPD patients. All children who met the definitions of FD, HL and OPD were included in group 4 (Table 1).
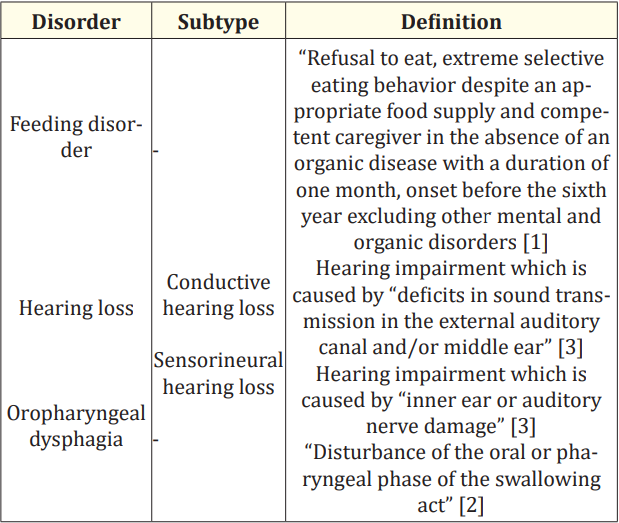
Table 1: Definitions.
Investigators extracted data from SAP ERP 6.0. Study data were collected using REDCap, a secure web-based application designed to manage online studies and databases [19]. We used SPSS version 27 (IBM SPSS statistics for windows, version 27.0) for statistical analysis under the strictest data security conditions (pseudonymisation). Analysts used simple descriptive statistics to illustrate patient demographics and clinical characteristics. Researchers presented categorical variables as frequencies and percentages. A p-value of <0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference.
This chapter includes a description of patient characteristics, the prevalence of HL, OPD and both impairments in children with FD and the secondary diagnoses. Prevalences and secondary diagnoses are shown for each of the 4 groups.
All demographic data are shown in table 2 and 3 and were divided according to the 4 categories of patients: 1 only FD; 2 FD and HL; 3 FD and OPD and 4 FD, HL and OPD, to look at the differences among the groups. The cohort consisted of n = 90 boys (50.3%) and n = 89 girls (49.7%). One hundred forty-eight children received audiometry (82.7%), n = 91 (50.8%) a FEES and n = 68 (38.0%) both.
All secondary diagnoses are shown in table 3 and the different groups. There were three children from the groups 3 (FD and OPD) diseases of the subgroups are listed in the supplement Tables S1- and 4 (FD; HL and OPD) who never experienced nasogastric probe S5. Additionally, we detected that probing was present in all four or tube feeding. For more information, see the supplementary Figures S1-S4.
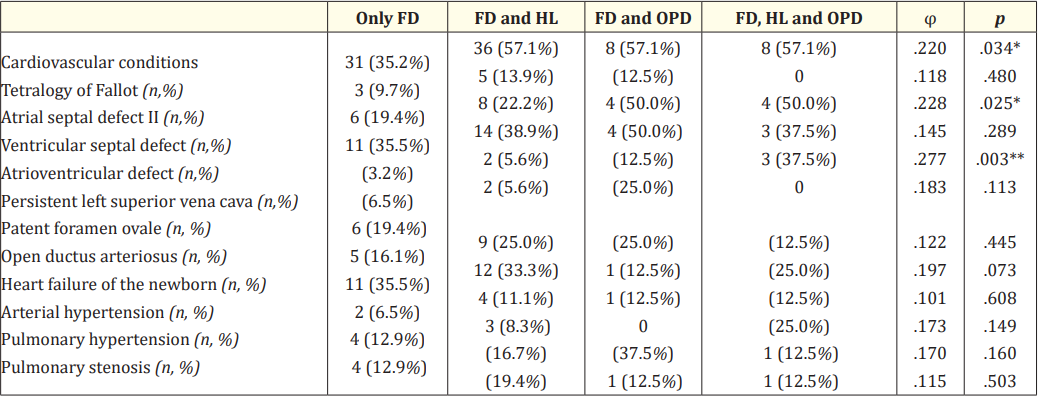
Table S1: Cardiovascular conditions.
Note: *p <.05, **p <.01, ***p < _.001.

Table S2: Neurological abnormalities.
Note: *p <.05, **p <.01, ***p < _ .001

Table S3: Malformations.
Note: *p <.05, **p <.01, ***p < _ .001

Table S4: Growth and nutritional impairments, allergies.
Note: *p <.05, **p <.01, ***p < _ .001.

Table S5: Other conditions and disorders.
Note: *p <.05, **p <.01, ***p < _ .001.

Figure S1: Probing* in general.
(coloured)
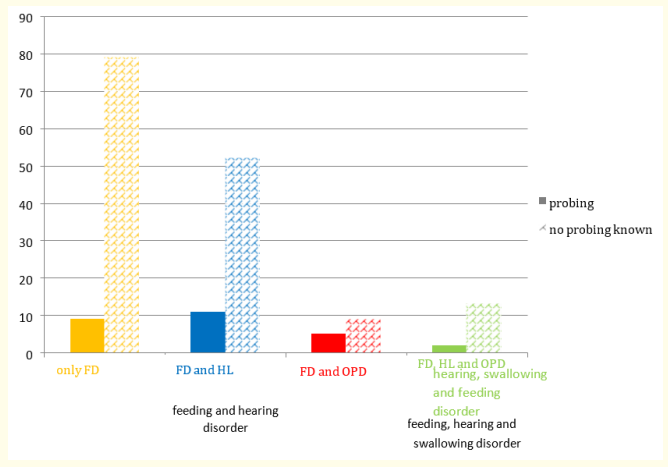
Figure S2: Nasogastric probe at first presentation, absolute number.
(coloured)
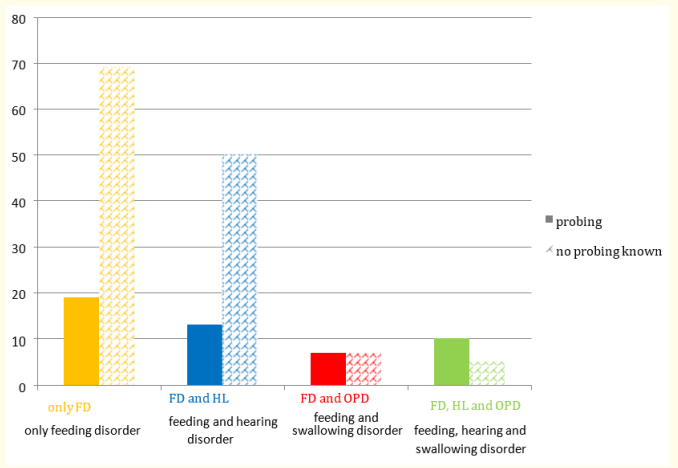
Figure S3: Probing* at OPD diagnostics, absolute number.
(coloured)
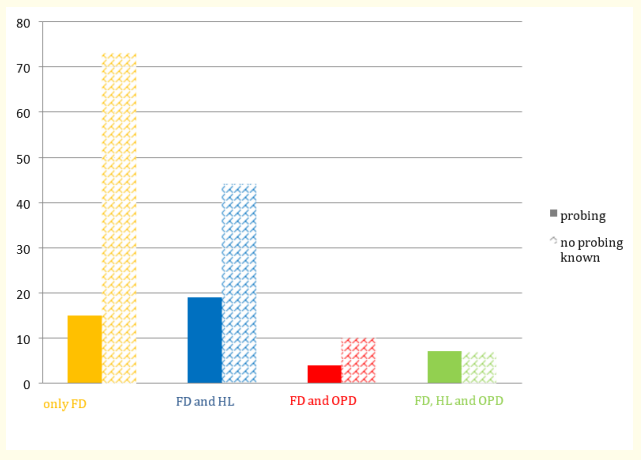
Figure S4: Probing* at audiometry, absolute number *probing in our cohort: nasogastric probe, PEG, other. Cardiovascular conditions.
The data of the newborn hearing screening are also presented eight children (52.8%) had an abnormal newborn hearing screenin table 2 and are known for 144 children (80.4%). Of these, 47 ing in the cohort with FD and HL. (Table 2 and 3). participants had abnormal screening results (32.6%). Twenty-eight children (52.8%) had an abnormal newborn hearing screening in the cohort with FD and HL. (Table 2 and 3).
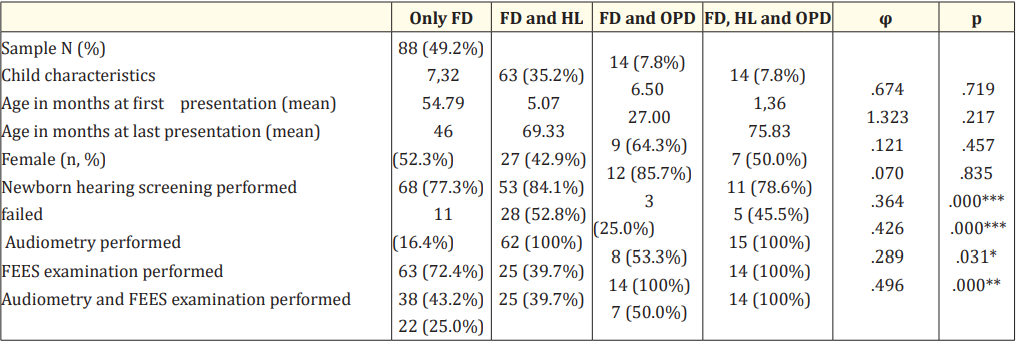
Table 2: Demographics (N = 179).
Note: *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < _ .001
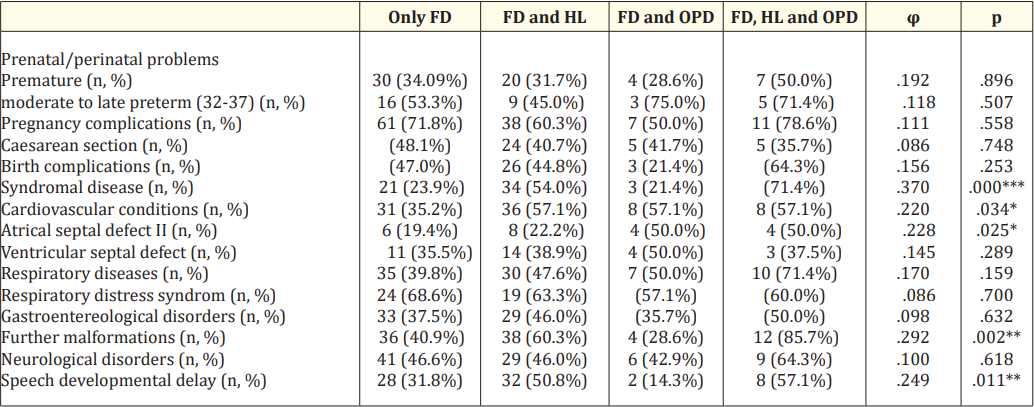
Table 3: Perinatal problems, secondary diagnoses, hospitalizations (N = 179).
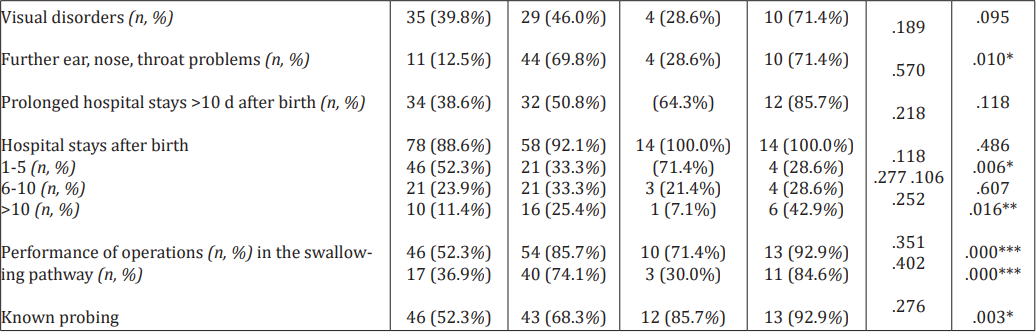
Table 4
The unequal distribution of the groups can be seen in the Venn diagram (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Venn diagram illustrating the degree of overlap between feeding disorder (FD), hearing loss (HL) and oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD).
Eighty-eight children (49.2%) experienced FD only.
Sixty-three children (35.2%) had both FD and HL. Pregnancy complications affected n = 38 (60.3%) children. Cardiovascular conditions were found in n = 36 (57.1%).
Fourteen patients (7.8%) were diagnosed with additional OPD. Cardiovascular conditions affected n = 8 (57.1%) and respiratory diseases n = 7 (50.0%) children.
Fourteen children (7.8%) were identified with all three impairments
Syndromal diseases were described in n = 10 (71.4%) children. Cardiovascular conditions affected n = 8 (57.1%) children and neurological diseases were found in n = 9 patients (64.3%). The cohort with all disorders had the highest percentages of secondary diagnoses and other abnormalities.
This chapter interprets the prevalences, secondary diagnoses and makes assumptions about associations. It also includes clinical implications, future study recommendations and limitations.
To our knowledge, our study is the first that describes the high prevalence of hearing loss (HL) in a larger cohort of infants with a diagnosed feeding disorder (FD), independent of a specific underlying disease, as a primary study concern and that draws attention to the relationship between FD, HL and oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD).
The prevalence of HL in our study (n = 77 (43.0%)) was significantly higher than in the general population (2,7/1000 26).
The high number of children with HL can support the assumption about an association between FD and HL. This connection was also indicated in the studies by Adams-Chapman., et al. [1] and Malas., et al. [27]. Common risk factors, such as cardiovascular conditions, may play a role in this association. A recent study by Gopineti., et al. [18] with 172 children showed that HL is more common in a paediatric population undergoing heart surgery.
Additionally, it should be emphasised that many children develop HL over time, despite unremarkable results in the newborn hearing screen assessment. Children with FD are likely predisposed to congenital and acquired hearing loss. Thinking in the other direction, it is conceivable that children with HL develop FD over time due to impaired communication. Further research is required on this point.
Interestingly, the prevalence of children with both FD and OPD was lower than expected. This observation may be because we included children in the “oropharyngeal swallowing and feeding disorder group” only if a disorder of the oral or pharyngeal phase was recognisable in the Flexible Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) examination at one point, concordant with the definition mentioned above.
Compared with the number of patients who had only swallowing and feeding disorder, it was noticeable that a relatively high number of children (n = 14) were diagnosed with all three disorders. Thus, there may be an association between all three impairments. Probable reasons for the simultaneous occurrence of the diagnoses are similar predictors. In the literature, the co-occurrence of HL and OPD is mentioned for children with CHARGE [12] and Noonan syndrome [32] for example. Syndromal diseases are important risk factors for developing FD, HL and OPD in combination [40].
Additionally, the high number of children with tube feeding is striking. Of course, this is more a consequence of the multiple underlying diseases [11]. Notably, our study includes three children diagnosed with OPD who never received tube feeding. Presumably, early diagnosis of our patients was sufficient for timely and adequate treatment with conservative measures, such as logopaedic swallowing training.
Surprisingly, a large number of preterm infants were moderate to late preterm rather than very and extremely preterm, contrary to our assumption. On the one hand, many authors have reported that feeding disorders are more common among extremely and very preterm children [10,30]. On the other hand, the observational study of 378 children [21] and the meta-analysis of 4381 children [31] confirmed that feeding problems occur more often in premature infants, regardless of their degree of prematurity.
The simultaneous occurrence of both feeding and swallowing disorders has been described in several surveys [14,33,40], in contrast to the unexplored connection between FD and HL. To our knowledge, our study is the only one that draws attention to the high prevalence of HL in infants with FD as a primary study objective and the possible relationship between FD, HL and OPD in a single study. This is the greatest strength of our investigation because it is essential to make the appropriate medical staff aware of this issue. It should also be emphasised that FEES has already been carried out on very young children in our centre, which is not the norm. Further advantages of this investigation are the detailed description of secondary diagnoses and the fact that we have not focused exclusively on one syndromal disease.
Targeting the increasing number of children with FD and HL is essential for clinicians. This study makes new conclusions for paediatricians, child psychiatrists, psychologists and all other responsible persons that hearing function must be regularly examined when treating children with FD. Additionally, these results highlight to otolaryngologists that exploration of clinical signs of feeding disorder in children with HL is required to initiate additional treatment (e.g., logopaedic, child-parent-psychotherapy).
Newborn hearing screening is always advisable. Furthermore, regular hearing examinations and interventions are necessary at different developmental stages during early childhood [5,29] for children with FD. This is crucial even if the newborn hearing screening was unremarkable. Especially in children with cardiovascular disorders or syndromal diseases, recurrent hearing tests are necessary. The current study of Gai., et al. [16] also mentions how important early and therapeutic services are for infants with HL. In contrast to our study, the investigation of Gai., et al. [16] focuses on hearing impairments as a result of defected genes.
Second, the question arises as to whether FEES examinations could be reduced, since OPD was much rarer in our investigation. Children at risk, for example with cardiovascular or respiratory diseases, should be screened.
The limitations of this study include its retrospective design and the fact that researchers collected data from children with only FD. Another area for improvement was that data could only be found from children who were first treated by child psychiatrists and then from otolaryngologists and unfortunately not in the reverse order. Due to the reasons mentioned, analysts could not perform some statistical tests. It was impossible to calculate the important associations to accept or reject the hypotheses.
Furthermore, the present ICD-10 diagnosis F98.2 [13] was used, lacking a description of previous diseases. However, in our study, the number of secondary diagnoses is very high for almost every child. The ICD-10 classification [13] was used in our survey because it is a good method of distinguishing between a feeding problem and a severe psychiatric eating disorder [17]. Moreover, experimenters took the data from a large tertiary centre, partly composed of a referral population, which may have generated an overassessment of the incidence of all three conditions. As this centre is specialised in treating feeding disorders in children with a wide range of different and complex paediatric conditions, it is challenging to study only the relationship between FD and other diagnoses, irrespective of pre-existing conditions.
A prospective cohort study with a longer follow-up should now be conducted to investigate the relationships further. Starting with the collection of newborn hearing screening data, children should be examined for the three disorders at different time points over several years. Long-term effects, the recording of language development, social and psychological problems should also be examined more closely. In addition, a control group and a larger cohort are necessary to perform various statistical tests, to calculate the associations and to identify risk factors using logistic regression.
This study described the prevalence and relationships of HL and OPD among children with FD aged between 0 and 6 years. The most significant advantage of this study is that it addresses a knowledge gap, as the topic has yet to be researched. To summarise, HL is common in children with FD. The results of the investigation indicated the significance of being aware of all three disorders, especially in infants and young children with multiple risk factors. An interdisciplinary concept involving child psychiatrists, child psychotherapists and otolaryngologists at an early stage of treatment is recommendable. This is important to obviate subsequent developmental difficulties and to contribute to positive growth and health. Further studies are needed to investigate the associations.
We thank the staff of the SKKIPPI – Team: Ms Sprengeler, Hannah Hächer, Marlene Leffler; the research team: Mr. Keil and Mr. White; other doctors of the clinic: Mrs Martin; the Phoniatrics and Audiology-Team: Mrs Röhricht, Mr Vogt and the data management team: Mr Meigen und Mrs Abel for their assistance.
None.
Reasonable requests for access to the datasets generated during and/or analysed during current study can be made to the research data team of the department (forschungsdaten@medizin. uni-leipzig.de), preferably by contacting the corresponding author.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Copyright: © 2023 Lina Viktoria Benkhardt., et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ff
© 2024 Acta Scientific, All rights reserved.