Davood Amirkashani*
Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Ali Asghar Children Hospital, University of MedicalSciences (IUMS), Tehran, Iran
*Corresponding Author: Davood Amirkashani, Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Ali Asghar Children Hospital, University of MedicalSciences (IUMS), Tehran, Iran.
Received: November 21, 2020; Published: December 10, 2020
Citation: Davood Amirkashani. “Overview About What We Need to Know About DKA, Pathology, Symptoms and Treatment ”. Acta Scientific Paediatrics 4.1 (2021): 09-10.
The most serious complication of type 1 diabetes is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), though it can occur in patients with type 2 but less common. Basic pathology in DKA is hypo insulinism or lack of effective insulin action followed pathologic cascade of events in 3 pathways include;
According to simple description of physiopathology, you can guess some symptoms of the patients with DKA.
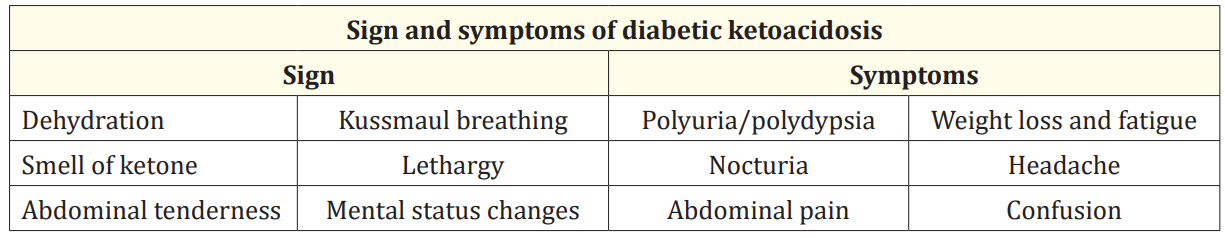
Table 1
Appearance of any symptoms depend on how much patient is delayed to hospital.
DKA is an emergency. If left untreated, it can lead to coma and even death. Therefore if your patient has above symptoms, immediately call emergency service. Before coming of emergency, firstly keep your calmness and hold head your patient up. You must not inject insulin your patient at all. Insulin injection in this situation may exacerbate brain edema. using of oxygen maker in home before hospital admission is beneficial if your patient has respiratory distress. It is preferred keep your patient fast, because decrement in consciousness level, increase risk of aspiration.
Initial investigation is airway, breathing and circulation assessment. Though decrement of insulin is basis of DKA, first medical therapy in hospital is fluid and electrolyte replacement with normal saline that help to fade out acidosis and hyperglycemai. Then after first hour, insulin therapy will be start. Treatment with bicarbonate must be avoided as much as possible. Electrolyte and blood gas will be monitored and will be corrected by hydration and insulin. If Whenever treatment result to eliminate symptoms, fluid and food eating will be resume.
If your children is known case of diabetes mellitus, there is always concern about DKA appearance. Therefore it is very important, insulin injection must do with every meal time and it is necessary blood glucose assay before and 2 hour after meal time. Sometimes blood glucose checking should be done frequently like as infectious periods. If blood glucose levels are frequently more than normal target range according to every age, may need to increment insulin dosage, if you know it or after your medicine consultation.
Also if there is strips for checking of urine ketones, it can inform you about DKA.
It is important we should know, in primary steps, may patient do not have any symptoms of DKA. Because of this, frequent blood glucose checking and urine ketones strips can help recognize DKA in preliminary.
we advise parents, learn how use urine ketone strips and when-
ever urine ketone showed positive bands feel danger for children with T1DM.
When your children with T1DM, involved by unexplained nausea and vomiting with or without abdominal pain, inappropriate lethargy, headache, breath difficulty call your physician or refer to hospital immediately even blood glucose not be high.
Unfortunately, almost 25% children with T1DM, firstly present with DKA, while her or his parents have not any information about DKA and may cause delay in take treatment on time and result morbidity and even mortality.
Therefore education about symptoms of DKA may help to save life a children.
For additional information about DKA you can refer to BSPED Interim Guideline for the Management of Children and Young People under the age of 18 years with Diabetic Ketoacidosis and care. diabetesjournals.org.
Copyright: © 2021 Davood Amirkashani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ff
© 2024 Acta Scientific, All rights reserved.