Maksudur Rahman1*, Kinkar Ghosh2, Md Mahbubul Hoque3 and M Monir Hossain3
1 Associate Professor, Neonatology, Bangladesh Institute of Child Health (BICH),
Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital, Bangladesh
2
Epidemiologist, Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital, Bangladesh
3
Professor, Neonatology, Bangladesh Institute of Child Health (BICH), Dhaka Shishu
(Children) Hospital, Bangladesh
*Corresponding Author: Maksudur Rahman, Associate Professor, Neonatology, Bangladesh Institute of Child Health (BICH), Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital, Bangladesh.
Received: July 09, 2020 ; Published: September 11, 2020
Citation: Maksudur Rahman., et al. “Incidence of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) of Neonates at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh”. Acta Scientific Paediatrics 3.10 (2020): 11-16.
Background: COVID-19 has become global pandemic. It affects mainly adult with serious devastating effect in some cases particularly those with chronic comorbidities. It is less common in children and rare in neonate. But to date with increasing surveillances number of neonates with COVID -19 are increasing.
Methods: This cross sectional study was conducted from April 2020 to June 2020 at Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital in Bangladesh. All admitted neonates with COVID-19 were taken as cases. Neonates with suspected COVID-19 were tested for SARS-CoV2 virus by RT- PCR. Criteria for test were baby born to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 mother, exposed to relatives infected with COVID-19, related with cluster outbreak, with abnormal clinical courses such as respiratory distress, not responded to conventional treatment and abnormal chest x-ray. Data regarding gestational age, birth weight, gender, and positive cases and other findings were collected and analyzed. Statistics analysis was done by SPSS version 17.
Results: During this study period total 1007 neonates were admitted. Among them 20 (2%) cases were COVID-19. Among the cases with covid19 male were 13 (65%) and female 7 (35%). Male and female ratio was 1.9:1. Term baby was 17 (85%) and preterm 3 (15%). Mean weight were 2618 ± 235 gms. Eight (40%) cases with COVID 19 lived in Dhaka and 12 (60%) cases in outside of Dhaka. Only 2 (10%) cases were positive for SARS- CoV2 virus by RT- PCR within 3 days but after 24 hours of age. Four (20%) and 14 (70%) cases were test positive at day 4 - 7 and 8 - 28 days respectively. Most of the diseases associated with COVID-19 belonged to neonatal medicine (16,80%) and only 4 (20%) cases were associated with surgical diseases. In neonate two or more diseases coexist in same cases. Sepsis was present in 4 (20%) cases with COVID -19. Perinatal asphyxia and pneumonia both were present in 3 (15%) cases.
Conclusion: In this study the incidence of neonates with COVID-19 was 2% among the hospitalized neonates. This implies that neonates also be affected with COVID-19 and it should be properly addressed for management of neonates with COVID-19 as well as for prevention of community transmission of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Corona Virus; Incidence of COVID-19
Recently, there was an outbreak of viral pneumonitis in Wuhan, Hubei, China in December 2019 [1-3]. It then has become global pandemic [1-3]. This disease is caused by a novel beta coronavirus species, the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). It was finally renamed as SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2) and the disease named as COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) [1-3].
There are few published data regarding COVID-19. Moreover, It is less common in children and rare in neonate [4,5]. The first cases of neonate with covid-19 was found in china on first February 2020 [3]. Then 3 cases of neonatal COVID-19 were identified in china up to February 2020 [2]. In Iran first neonatal case was identified also at February [6].
Due to enhance surveillance of COVID-19 and availability and accessibility of rapid genetic amplification assays, a growing number of pediatric cases with COVID-19 have been confirmed in Wuhan and other areas [1,5,7]. Now number of neonates with covid19 are increasing in different area of the world [2,8,9].
The SARS-CoV-2 causes variety of clinical symptom especially in respiratory system like mild upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, severe pneumonia. Sometime this infection rapidly spreads causing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), shock and death [1,2,10]. Most of the children are asymptomatic and have mild clinical manifestation of this disease unlike adult. Neonates with COVID-19 even have less clinical manifestations [2,5].
As increasing the publication, it is found that newborns are susceptible to this disease from COVID-19 positive mother and community, and viruses are detected for a prolonged period; therefore, newborns might play a role in community transmission [1].
So it is important to see the incident of neonatal with COVID-19 so that management of the disease can be taken more appropriately and transmission to heath personnel as well as family member can be prevented.
This cross sectional study was conducted from April 2020 to June 2020 at Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital, one of the largest children hospital in south Asia. This is a multi-disciplinary tertiary care hospital which is not designated for COVID-19. The ethical clearance was taken from hospital authority and appropriate written consent was taken before each intervention from parents of neonates. All neonates who were admitted at this hospital for different reasons were assessed for any suspicion of COVID-19. Clinical suspicions were made by baby born to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 mother, exposed to relatives infected with COVID-19, related with cluster outbreak and with abnormal clinical course such as respiratory distress not responded with conventional treatment and abnormal chest x-ray. Neonates with suspected covid-19 were tested for SARS-CoV2. Nasal swab was taken with a swab stick by heath technologist with all aseptic precaution and wearing PPE (Personal protective instrument). Swab stick (FLOQSwabs, copanflocked swabs) was introduced into nose at a length similar to half way between ear lobule to same side ala nasi of nose. Then proximal broken swab stick was put into a tube (Falcon tube) filled with RNA shield fluid that inactivate virus. Finally, RT- PCR (Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction) was done for detection of nucleic acid of virus. The method used for this test was real time PCR for SARS-CoV2 and instrument used was Rotor Gene Q (5 plex HRM Analyzer), Qiagen GmbH. All tests were done in a government approved laboratory. All positives cases were evaluated and cases were either discharged who had features of improvement or referred to COVID-19 designated hospital. The discharged neonates were given proper counselling for breastfeeding, isolation care of baby and also isolation for attendants.
In this study main outcome variable was number of test positive cases for SARS-CoV2. We collected data on gender, birth weight, gestational age, resident, and associated diseases. The data were entered and analyzed using Statistical Package of Social Science SPSS, version 17. The descriptive statistics such as frequencies, percentages were calculated to summarize nominal and ordinal data, while mean and standard deviation to describe numerical variables.
During this study period total 1007 neonates were admitted. Among them 20 (2%) cases were COVID-19 (Figure 1). Among the cases with covid19 male were 13 (65%) and female 7 (35%). Male and female ratio was 1.9:1. Term baby was 17 (85%) and preterm 3 (15%). Mean weight were 2618 ± 235 gms. Eight (40%) cases with covid19 lived in Dhaka and 12 (60%) cases in outside of Dhaka (Table 1). Only 2 (10%) cases were positive for SARS -CoV-2 virus by RT- PCR within 3 days but after 24 hours of age of neonates. Four (20%) and 14 (70%) cases were test positive at day 4 - 7 and 8 - 28 days of age of neonates respectively (Table 2). Most of the diseases associated with COVID-19 belonged to neonatal medicine (16,80%) and only 4 (20%) cases were associated with surgical diseases. In neonate two or more diseases coexist in same cases. Sepsis was present in 4 (20%) cases with COVID-19. Perinatal asphyxia and pneumonia both were present in 3 (15%) cases (Table 3).
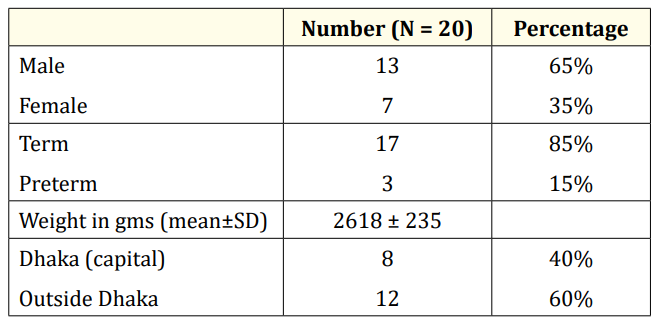
Table 1: Distribution of cases according to gender, gestational age, weight and resident.
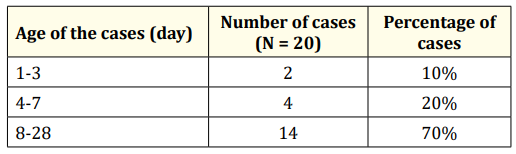
Table 2: Time of first test positive cases for SARS-CoV 2 by Rt-PCR. SARS severe acute respiratory syndrome, COV 2 corona virus 2, RT- PCR reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction.

Figure 1: Hospital incidence of neonates with COVID-19.
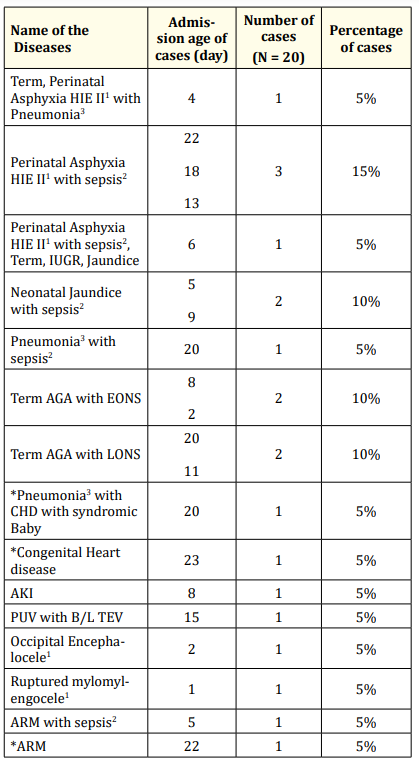
Table 3: Associated diseases with COVID-19. HIE: Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy; IUGR: Intra Uterine Growth Retardation; AGA: Appropriate for Gestational Age; EONS: Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis; LONS: Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis; CHD: Congenital Heart Disease; AKI: Acute Kidney Injury; PUV: Posturetral Valve; B/L: Bilateral; TEV: Telipes Equenovarus, ARM: Anorectal Malformation; *late preterm; 1 perinatal asphyxia 3 cases, 2 sepsis 4 cases, 3 pneumonia 3 cases.
This cross sectional study was conducted from April 2020 to June 2020 at Dhaka Shishu (Children) Hospital. All admitted neonates with COVID-19 were taken as cases. During this study period total 1007 neonates were admitted. Among them 20 (2%) cases were COVID-19.
The first case of COVID-19 was detected in Bangladesh at 8th
March 2000 who is adult [11]. We started Rt-PCR for COVID-19 at this hospital at the month of April in this year.
Worldwide the incidence of covid19 in children is very few in contrast to adult even rare in neonates [12]. The first children affected by COVID-19 in china on January, 2020 [13]. Liu., et al. Showed in their study that the incidence of COVID-19 in paediatric age group was 1.6% among the hospitalized children with respiratory infection [14]. Another study done by Tu., et al. showed in their study that the incidence of COVID-19 in children was 0.6% among the confirmed cases of all age group [15]. At the month of February several study showed that neonates were also affected by COVID-19 [3,16]. The first neonate with COVID-19 was identified in first February 2020 which was published by Wang S., et al. [3]. Then 3 neonates with COVID-19 were identified at that month which was published by Choi., et al. [1]. At that time in different countries neonates also were affected with COVID-19. In Iran first case of neonatal COVID-19 was found at this month [6]. As increasing the publication on neonate with COVID-19, the number of neonate with COVID-19 is increasing in the world [1,6]. But still it is very few unlike adult [7]. The cause of less neonatal COVID-19 may be the presence of less number of ACE2 receptor in their respiratory tract and their more stronger innate immunity than adult [17,18]. Surprisingly we see more number of neonates with COVID-19 (2%, 20 cases) in this study. The neonatal COVID-19 is increasing. It may due to increase community transmission, and household contact including mother of this virus. Though the transmission of SARSCoV 2 virus through placenta and breast milk is still definitely unidentified [19-21].
Among the cases with COVID-19 male were 13 (65%) and female 7 (35%). Male and female ratio was 1.9:1. Term baby was 17 (85%) and preterm 3 (15%). Mean weight were 2618 ± 235 gms. It was seen that in this study male was predominantly affected by COVID-19. The cause of this finding still unknown. In this study it was found that term and normal weighted neonate were affected more.
But regarding gender and gestational age, no statistical comparison was done. In one study, it was found no significant sex predominant in children [5]. In this study eight (40%) cases with COVID-19 lived in Dhaka and 12 (60%) cases in outside of Dhaka. This implies that only in Dhaka (capital of Bangladesh) affected cases were more as a single city than rest of the districts. In another study it was found that COVID-19 affected cases more in city [5].
In our study 2 (10%) cases were positive for SARS-CoV-2 virus by RT PCR within 3 days but after 24 hours of age of neonates. Four (20%) and 14 (70%) cases were test positive at 4 - 7 and 8 - 28 days of age of neonates respectively. It may imply that most of the cases were affected from community or from family members. In one study it was found that children were affected from community or household contact [16].
It was found in this study that most of the diseases associated with COVID-19 belonged to neonatal medicine (16/20, 80%) and only 4/20 (20%) cases were associated with surgical diseases. In neonate two or more diseases coexist in same cases. Sepsis was present in 4 (20%) cases with COVID-19. Perinatal asphyxia and pneumonia both were present in 3 (15%) cases.
This hospital is not a COVID-19 designated hospital and all patient were out born. Initially all patient was managed in another hospital and later referred to this hospital. So newborn with any conditions or diseases was admitted. In this study it was not said that whether associated conditions like sepsis and pneumonia were caused by COVID-19 or these conditions were associated with neonatal COVID-19. Several study showed COVID-19 presented with respiratory distress, sepsis like manifestation etc. [5,10]. In this study exposer history and outcome of cases could not be evaluated properly.
We have found relatively significant number of neonates with COVID-19 in this study. These infant may be a source of transmission of this disease. So, we should give proper emphasis on test, tracing and management of neonatal COVID-19 like adult.
In this study the incidence of neonates with COVID-19 was 2% among the hospitalized neonates. This implies that neonates also be affected with COVID-19 and it should be properly addressed for management of neonates with COVID-19 as well as for prevention of community transmission of the disease.
The authors are grateful to the CHRF (Child Health Research Foundation) providing facilities to carry out the research work.
Dr. Maksudur Rahman conceptualized, gathered and analyzed the data. Mr. Kinkor Gosh helped collecting the data. Prof. Dr. Md. Mahbubul Hoque supervised and contributed significantly to the writing of the manuscript. Prof, Dr. M. Monir Hossain gave necessary inputs in designing the manuscript. All authors discussed the methodology and results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest declared none.
Copyright: © 2020 Maksudur Rahman., et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ff
© 2024 Acta Scientific, All rights reserved.