Kunal Joon*
Noida International Institute of Medical Sciences, Haryana, India
*Corresponding Author: Kunal Joon, Noida International Institute of Medical Sciences, Haryana, India.
Received: September 23, 2024; Published: October 13, 2024
Citation: Kunal Joon. “Mechanism of ligand to trigger immune response". Acta Scientific Microbiology 7.11 (2024):07-10.
It deals with how the Ligands interact and activate the Natural Killer cells and other T cell to act and cause release of cytokines and also discuss the mechanism of action.
Keywords: Cytokines; Flowcytometery; Interleukin -8; Immunofluroscence; Immunophotometery
Immune cell surface consist of the receptors which consist of the ligand binding receptor to which ligand bind and trigger the [1] compliment pathway and trigger the immune response and cytokine response and release of cytokines in the body and trigger the immune response [2].
Experiment
Study of the ligand response through experimentation study.

Figure 1
It demonstrates the ligand concentration increases the response of the Natural Killer cells increasing and the graph and as the [3] concentration of ligand increases graph goes upward exponentially and also in Figure mechanism of the ligand attachment to receptor is shown and through flow cytometery the action is shown [4].
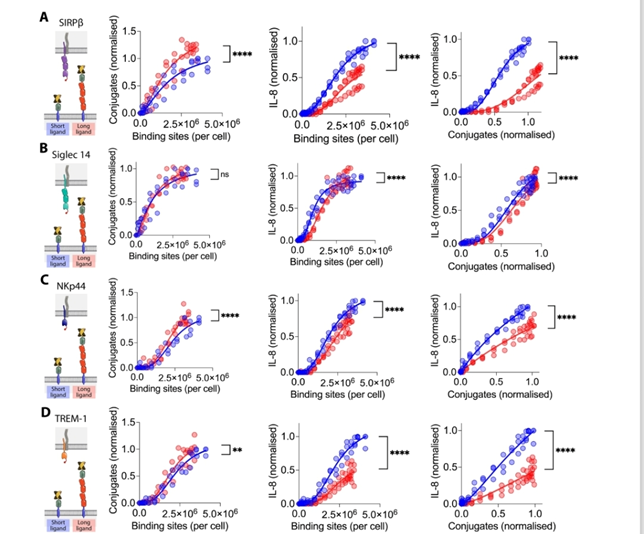
Figure 2
This Figure shows effect of ligand on four receptors that is A) SIRPß In this as ligand concentration increases graph move towards the saturation b) Siglec14 in this there is a direct exponential phase and the saturation phase no lag phase c) NKp44 in this the phase goes normally with lag phase exponential and saturation phase [5]. d) TREM1 in this phase there is a long lag phase in which during starting there is no effect and as there is rise there is short log phase in which there is less effect and as there is increase in concentration there is sudden increase and switch over to exponential phase [6].
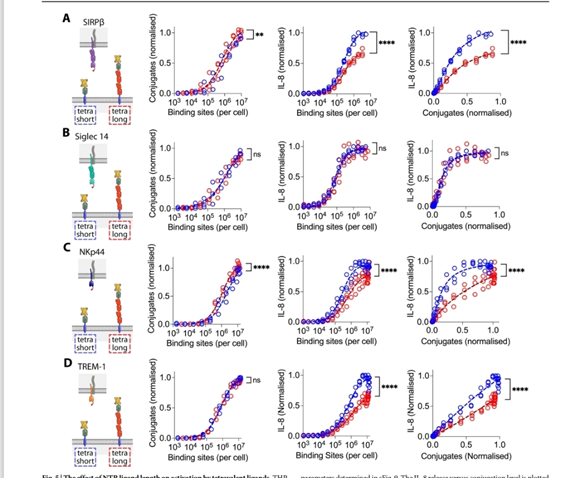
Figure 3
This is shows the conjugation versus IL8 graph and shows in which there is increase in the conjugation and multiple increase in the tetra long in all the cells and we see the exponential increase in the IL8 cells in the concentration and lead to the increased IL8 and also there is a saturation phase [7].
Ligand stimulate the Natural Killer cells and stimulate the release of IL8.
Construction methods
CD80 anchor (short). METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD YPY [8]
DVPDYATGGSAHIVMVDAYKPTKGGSGGS HVSEDFT
WEKPPEDPPDSKNTLVLFGAGFGAVITVVVIVVIIKCF
CKHRSCFRRNEASRETNNSLTFGPEEALAEQTVFL
CD80 anchor (long). METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD YPY
DVPDYA TGGSAHIVMVDAYKPTKGGSGGS KVVLGK
KGDTVELTCTASQKKSIQ FHWKNSNQIKILGNQGSFL
TKGPSKLN D D ADSRRSLWDQGNFPLIIKNLKIEDSDT
YICEVEDQKEEVQLLVFGLTANSDTHLLQGQSLTLTL
ESPPGSSPSVQCRSPRGKNIQGGKTLSVSQLELQDSG
TWTCTVLQNQKKVEFKIDIVVLAFQKASSIVYKKEGE
QVEFSFPLAFTVEKLTGSGELWWQAERASSSKSWITF
DLKNKEVSVKRVTQDPKLQMGKKLPLHLTLPQALPQ
YAGSGNLTLALEAKTGKLH QEVNLVVMRATQLQKNL
TCEVWGPTSPKLMLSLKLENKEAKVSKREKAVWVLN
PEAGMWQCLLSDSGQVLLESNIKVLPTRS HVSEDFT
WEKPPEDPPDSKNTLVLFGAGFGAVITVVVIVVIIKCF
CKHRSCFRRNEASRETNNSLTFGPEEALAEQTVFL
CD43 anchor. METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGDYPYDVPD
YATGGSAHIVMVDAYKPTKGGSGGS QESSGMLLVPM
LIALVVVLALVALLLLWRQR QKRRTGALTLSGGGKRN
GVVDAWAGPARVPDEEA TTTSGAGGNKGSEVLETEG
SGQRPTLTTFFSRRKSRQGSLVLEELKPGSGPNLKGEEE
PLVGSEDEAVETPTSDGPQAKDEAAPQSL
CD52 anchor. METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD YPYDVP
DYAT GGSAHIVMVDAYKPTKGGSGG SDTSQTSSPSAS
SNISGGIFLFFVANAIIHLFCFS
Strep-Tactin-SpyCatcher sequence. Strep-Tactin is underlined,
SpyCatcher is in italics and the polyaspartate sequence is in bold.
MAEAGITGTWYNQLGSTFIVTAGADGALTGTYVT
ARGNAESRYVLTGRYDSAPATDGSGTALGWTVAWKN
NYRNAHSATTWSGQYVGGAEARINTQWLLTSGTTEA
NAWKSTLVGHDTFTKVKPSAASDDDGDDDGDDDDS
ATHIKFSKRDEDGKELAGATMELRDSSGKTISTWISDG
QVKDFYLYPGKYTFVETAAPDGYEVATAITFTVNEQGQ
VTVNGKATKGDAHI
Strep-Tactin sequence. MAEAGITGTWYNQLGSTFIVTAG
ADGALTGTYVTARGNAESRYVLTGRYDSAPATDGSG
TALGWTVAWKNNYRNAHSATTWSGQYVGGAEARI
NTQWLLTSGTTEANAWKSTLVGHDTFTKVKPSAAS
Dead Streptavidin sequence. Bold amino acids mark substitutions in order to prevent binding to Strep tag II or biotin.
MAEAGITGTWYA QLG D TFIVTAGADGALTGTYE
AAVGAESRYVLTGRYDSAPATDGSGTALGWTVAWKN
NYRNAHSATTWSGQYVGGAEARINTQWLLTSGTTEA
NAWKSTLVGHDTFTKVKPSAAS
In this research we discussed about the how Ligands stimulate the Natural Killer cells and done comparison between ligand graph and the IL8 graph sideways and these are normal reports of person on giving ligands.
Ligands stimulate Natural Killer cells to release IL8 and other cytokines and can be used in the treatment of any outer drug reaction making release of IL against the drug to nullify it.
Copyright: © 2024 Kunal Joon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.